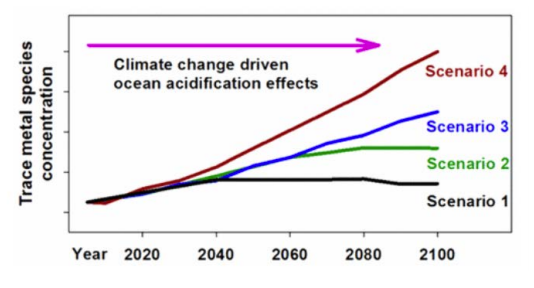
Under a peak emission by 2100, the model study predicted free ion Al, Fe, Cu, and Pb concentrations increase by factors of up to approximately 21, 2.4, 1.5, and 2.0, respectively. The metals usually remain organically complexed, have a lower sensitivity to such changes. Organically complexed Mn, Cu, Zn, and Cd concentrations fall by up to 10% and in the case of Fe, Co, and Ni rise by up to 14%. These small changes have high potential to alter the bioavailable fraction of the biologically active metals.
